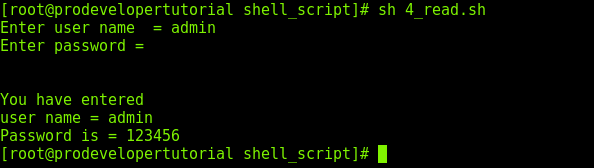
As shown above, while entering user name, the input is displayed. But while entering the password, the value is not displayed, because we have used “-s” option.
Example 3:
If you want to store multiple variables inside an array, use “-a” option in read function. “-a” option will instruct shell to read an array. Then while printing the value, display one by one by using the index value.
#!/bin/bash
echo “Enter multiple items”
read -a items
echo “Items : ${items[0]} ${items[1]} ${items[2]} ${items[3]} ”
Output:
Enter multiple items
pro developer tutorial
Names : pro developer tutorial
Example 4:
If you don’t give any variable name while using read command, then if any input provided by the user will go to a special variable called as “REPLY”.
#!/bin/bash
echo “Enter website name”
read
echo “The website name is $REPLY”
Output:
Enter website name
prodevelopertutorial.com
The website name is prodevelopertutorial.com