Question:
Given an array, print that array in reverse order.
Example:
Input : {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}
Output : {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Solution:
We can solve this problem by different ways, some of them are explained in this article are:
1. By using C++ STL
2. By taking a temp variable
3. By recursion.
Method 1: By using C++ STL
In C++ we have a “.reverse()” function, that will return the reverse order.
Below is the code for the same:
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
//visit www.ProDeveloperTutorial.com for 450+ solved questions
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector <int> v = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
cout << "The original vector is: " ;
for ( auto iter = v.begin( ) ; iter != v.end( ) ; iter++ )
cout << *iter << " ";
cout << endl;
// Reverse the elements in the vector
reverse (v.begin( ), v.end( ) );
cout << "Reverse of the vector is " ;
for ( auto iter = v.begin( ) ; iter != v.end( ) ; iter++ )
cout << *iter << " ";
cout<< endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
The original vector is: 1 2 3 4 5
Reverse of the vector is 5 4 3 2 1
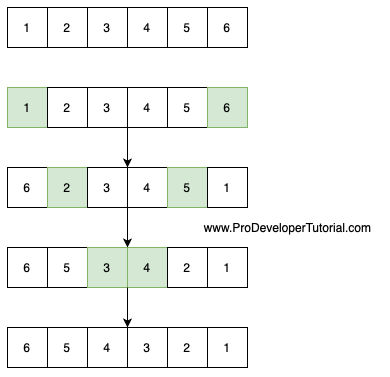
Method 2. By taking a temp variable / Iterative method / Two Pointer approach
Steps:
1. Call a function that will accept the array/ vector.
2. Get the start position and end position.
3. Swap the start and end elements
4. Increment start by 1 and decrement end by 1
Here the complexity will be O(n) as the loop will iterate number of element times.
This can be visualized as below:
Solution:
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
//visit www.ProDeveloperTutorial.com for 450+ solved questions
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void reverse_array (vector<int> &v)
{
int start = 0;
int end = v.size() - 1;
while (start < end)
{
int temp = v[start];
v[start] = v[end];
v[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
int main()
{
vector <int> v = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
cout << "The original vector is: " ;
for ( auto iter = v.begin( ) ; iter != v.end( ) ; iter++ )
cout << *iter << " ";
cout << endl;
// Reverse the elements in the vector
reverse_array (v);
cout << "Reverse of the vector is " ;
for ( auto iter = v.begin( ) ; iter != v.end( ) ; iter++ )
cout << *iter << " ";
cout<< endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
The original vector is: 1 2 3 4 5
Reverse of the vector is 5 4 3 2 13. By recursion
Another approach is by using recursion instead of iterative.
Here just swap the elements, and call the function recursively.
Make sure to include a start and end variable.
Here the complexity will be O(n) as the loop will iterate number of element times.
Solution in C++
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
//visit www.ProDeveloperTutorial.com for 450+ solved questions
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void reverse_array_recursively (vector<int> &v, int start, int end)
{
if (start >= end){
return;
}
int temp = v[start];
v[start] = v[end];
v[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
reverse_array_recursively(v, start, end);
}
int main()
{
vector <int> v = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
cout << "The original vector is: " ;
for ( auto iter = v.begin( ) ; iter != v.end( ) ; iter++ )
cout << *iter << " ";
cout << endl;
// Reverse the elements in the vector
reverse_array_recursively (v, 0, v.size()-1);
cout << "Reverse of the vector is " ;
for ( auto iter = v.begin( ) ; iter != v.end( ) ; iter++ )
cout << *iter << " ";
cout<< endl;
return 0;
}Output:
The original vector is: 1 2 3 4 5
Reverse of the vector is 5 4 3 2 1