Problem Statement:
You are given a binary tree, you need to traverse diagonal and print the nodes.
Example
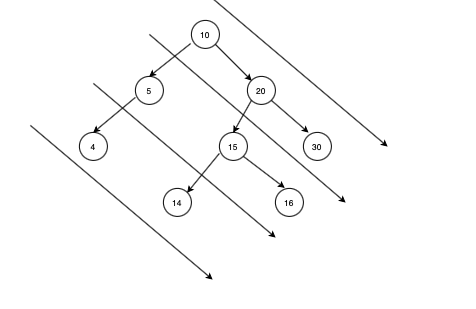
The diagonal traversal is :
10 20 30
5 15 16
4 14Solution
We shall use queue to solve the problem.
We follow below steps:
Enqueue root
when queue is not empty, dequeue
print
If it has a left child, enqueue it
Go to its right child
print it
Repeat the above steps.
Solution in C++
—————————————————————
#include <algorithm>
//visit www.ProDeveloperTutorial.com for 450+ solved questions
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// structure to hold binary tree node
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *left, *right;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
this->left = this->right = nullptr;
}
};
void diagonal_print(Node *root)
{
Node *temp;
Node *temp1;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
temp=q.front();
cout<<temp->data<<" ";
q.pop();
temp1=temp;
while(temp1)
{
//if left child exists EnQueue
if(temp1->left)
q.push(temp1->left);
//process all right children
temp1=temp1->right;
if(temp1)
cout<<temp1->data<<" ";
}
}
}
int main()
{
Node* root = nullptr;
/* Binary tree:
16
/ \
/ \
10 25
/ \ / \
/ \ / \
7 15 18 30
*/
root = new Node(16);
root->left = new Node(10);
root->right = new Node(25);
root->left->left = new Node(7);
root->left->right = new Node(15);
root->right->left = new Node(18);
root->right->right = new Node(30);
cout<< " Diagonal traversal of the binary tree is "<<endl;
diagonal_print(root);
return 0;
}
Output:
Diagonal traversal of the binary tree is
16 25 30 10 15 18 7