Example 1:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, k = 2
Output: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: 5->1->2->3->4->NULL
rotate 2 steps to the right: 4->5->1->2->3->NULLExample 2:
Input: 0->1->2->NULL, k = 4
Output: 2->0->1->NULL
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: 2->0->1->NULL
rotate 2 steps to the right: 1->2->0->NULL
rotate 3 steps to the right: 0->1->2->NULL
rotate 4 steps to the right: 2->0->1->NULLAlgorithm:
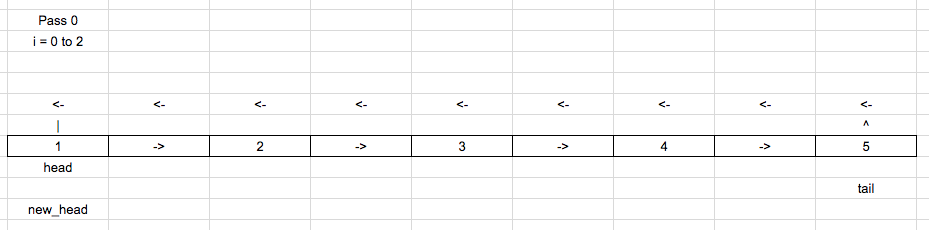
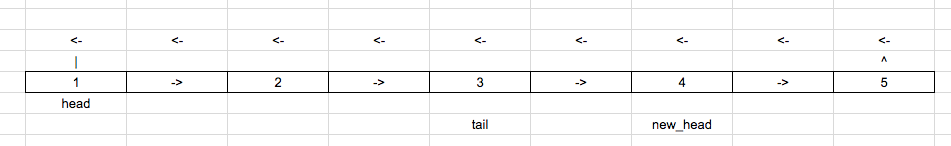
Take 2 pointers pointing to the head pointer.
new_head = tail = head
Get the length of the list.
Connect the end of the list to the starting of the list, making it a loop.
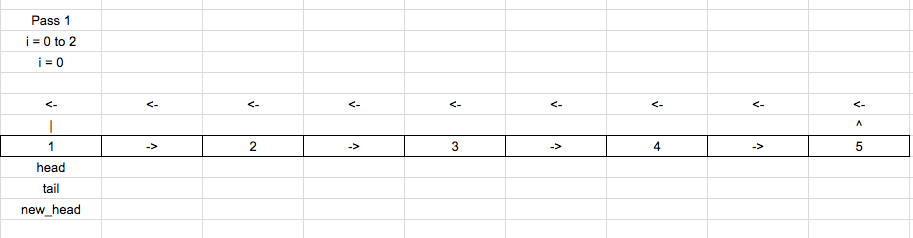
Get modulo(k, list_len) to avoid extra rotation.
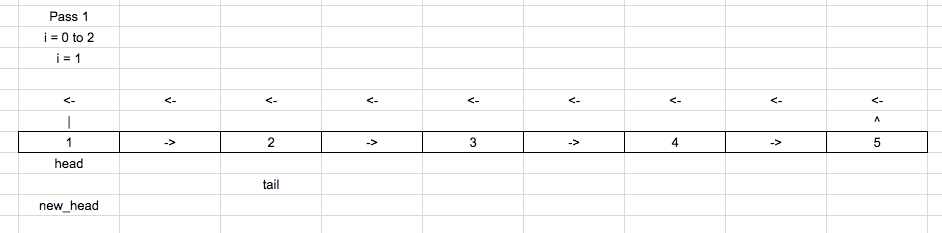
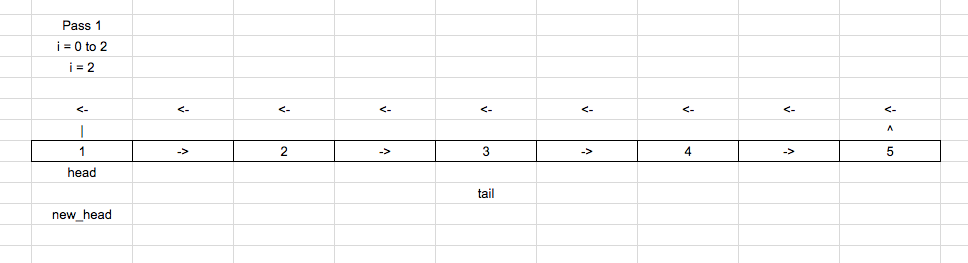
Move the tail pointer [len – k] times
Break the loop, and point the new_head to tail -> next.
Thus getting new head.
Let us understand with the help of an example:
Initial list:
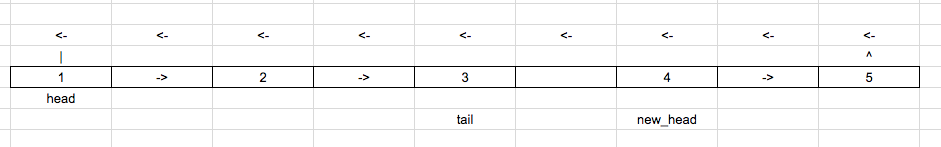
Now we come out of the loop, then perform
new_head = tail -> next.
Now we break the loop by “tail -> next = NULL”
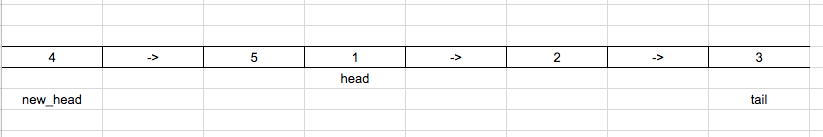
Our final list will look like below:
Solution in C++
/*
* File : rotate_k_nodes.cpp
* Author : ajay.thousand@gmail.com
* Copyright: @ prodevelopertutorial.com
*/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
void display_list(struct Node **head_pointer)
{
// take a reference to head pointer for navigation
struct Node *temp = *head_pointer;
while(temp != NULL)
{
if(temp->next != NULL)
printf("%d -> ", temp->data);
else
printf("%d", temp->data);
//navigate to next pointer
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
Node* rotate_k_nodes(Node* head, int k)
{
if(!head) return head;
int len=1; // number of nodes
Node *new_head, *tail;
new_head=tail=head;
while(tail->next) // get the number of nodes in the list
{
tail = tail->next;
len++;
}
tail->next = head; // loop the link
if(k %= len)
{
for(auto i=0; i<len-k; i++) tail = tail->next;
}
new_head = tail->next;
tail->next = NULL;
return new_head;
}
int main()
{
struct Node* result_node;
struct Node* newNode;
int k = 2;
struct Node* list_1 = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
list_1->data = 1;
newNode = (struct Node*) malloc (sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = 2;
list_1->next = newNode;
newNode = (struct Node*) malloc (sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = 3;
list_1->next->next = newNode;
newNode = (struct Node*) malloc (sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = 4;
list_1->next->next->next = newNode;
newNode = (struct Node*) malloc (sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = 5;
list_1->next->next->next->next = newNode;
list_1->next->next->next->next->next = NULL;
cout<<"The entered list is = "<<endl;
display_list(&list_1);
result_node = rotate_k_nodes(list_1, k);
cout<<"The list after rotating "<<k <<" times is = "<<endl;
display_list(&result_node);
}
Output:
The entered list is =
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
The list after rotating 2 times is =
4 -> 5 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3