Problem Statement:
You are given an undirected graph. You need to check if it is connected or not.
Example
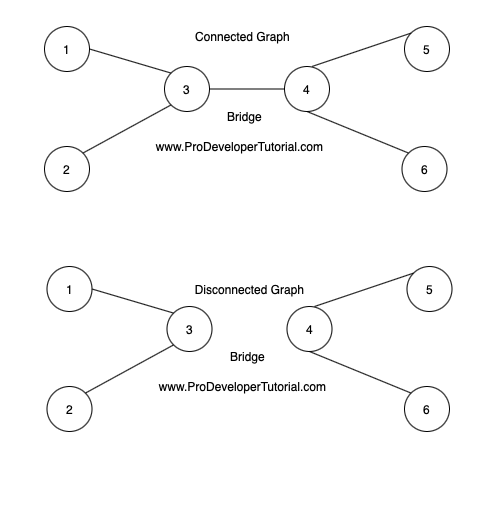
Solution
In the above image, the first graph is a connected graph, second is disconnected graph.
In a connected graph, there is always a path from any node to any other node in the graph.
We can solve this problem by using DFS.
We will have a boolean array visited[], then we pick a vertex and visit all the neighboring vertex.
After completion of DFS we check if all the vertices are visited.
Solution in C++
#include <algorithm>
//visit www.ProDeveloperTutorial.com for 450+ solved questions
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
class Graph
{
private:
int V;
list<int> *adj; // to hold adjacency list
void helper(int v, bool visited[]); // helper function for check_if_connected
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
void add_edge(int v, int w); // to add an edge to graph
bool check_if_connected(); // returns true if there is a cycle in this graph
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
// get the total number of nodes
this->V = V;
// initialize adjacency list for that number of nodes
adj = new list<int>[V];
}
void Graph::add_edge(int v, int w)
{
// add the edge to adjacency list
adj[v].push_back(w);
adj[w].push_back(v);
}
void Graph::helper(int v, bool visited[])
{
visited[v] = true;
list<int>::iterator i;
for(i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); i++)
{
int adjVertex = *i;
if ( visited[adjVertex] == false ){
helper(adjVertex, visited);
}
}
}
bool Graph::check_if_connected()
{
bool *visited = new bool[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
visited[i] = false;
}
helper(0, visited);
for (int i = 0; i <V ; i++)
{
if(!visited[i]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
Graph g(4);
g.add_edge(0, 1);
g.add_edge(0, 2);
g.add_edge(1, 2);
g.add_edge(2, 0);
g.add_edge(2, 3);
g.add_edge(3, 3);
if(g.check_if_connected())
cout << "Graph is connected";
else
cout << "Graph is not connected";
return 0;
}
Output:
Graph is connected