Example:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
This problem can be solved in 2 ways.
1. Iterative
2. Recursive.
1. Iterative solution.
In this solution, we need 3 pointers.
In this solution, we need 3 pointers. And initialize as shown below:
prev = NULL
Curr = head
Temp = NULL
So we iterate and reverse the list until the current is null. Below is the code used.
while(cur)
{
tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = tmp;
}Consider the example
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4


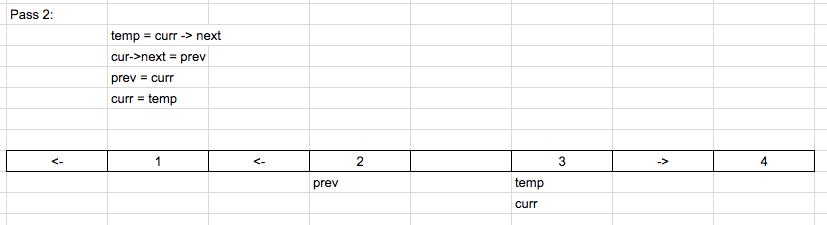
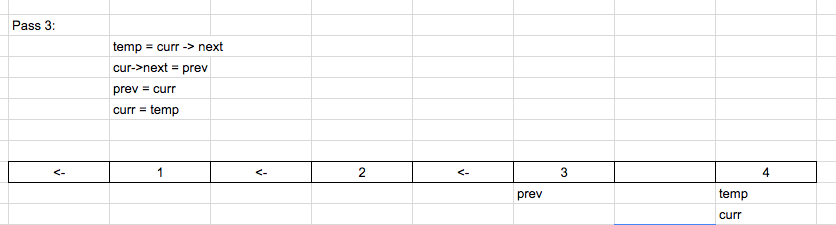
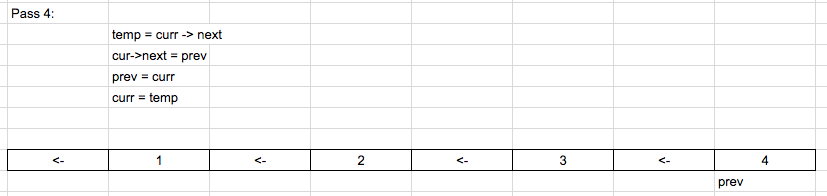
Solution in C++
/*
* File : reverse_linked_list.cpp
* Author : ajay.thousand@gmail.com
* Copyright: @ prodevelopertutorial.com
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
void insert_at_begenning ( struct Node **head_pointer, int data)
{
// allocate memory for new node
struct Node *temp_node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// assign the data to new node
temp_node->data = data;
// initialize the new node to point to NULL
temp_node->next = NULL;
// if this is the first pointer, then this is the head pointer
if (*head_pointer == NULL)
{
*head_pointer = temp_node;
}
else
{
// point the next of the present pointer to the head pointer
temp_node->next = *head_pointer;
//then move the reference of head pointer to the current pointer
*head_pointer = temp_node;
}
}
void display_list(struct Node **head_pointer)
{
// take a reference to head pointer for navigation
struct Node *temp = *head_pointer;
while(temp != NULL)
{
if(temp->next != NULL)
printf("%d -> ", temp->data);
else
printf("%d", temp->data);
//navigate to next pointer
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
Node* reverse_using_iterative_solution(Node* head)
{
Node *prev = NULL, *cur=head, *tmp = NULL;
while(cur)
{
tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return prev;
}
Node* reverse_using_recursive_solution(Node* head)
{
if(!head || !(head->next))
return head;
Node* reverse_list = reverse_using_recursive_solution(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return reverse_list;
}
int main()
{
struct Node *list_1 = NULL;
struct Node *result = NULL;
insert_at_begenning(&list_1,8);
insert_at_begenning(&list_1,7);
insert_at_begenning(&list_1,6);
insert_at_begenning(&list_1,5);
insert_at_begenning(&list_1,4);
insert_at_begenning(&list_1,3);
insert_at_begenning(&list_1,2);
insert_at_begenning(&list_1,1);
printf("Original Lis\n");
display_list(&list_1);
//result = reverse_using_iterative_solution(list_1);
//printf("The result list using iterative method is\n");
result = reverse_using_recursive_solution(list_1);
printf("The result list using recursive method is\n");
display_list(&result);
return 0;
}